Air pollution is a modern health challenge linked with heart disease, dementia, and chronic inflammation.
While reducing exposure is the ideal solution, growing research suggests that certain nutrients may help protect the body against some of its harmful effects.
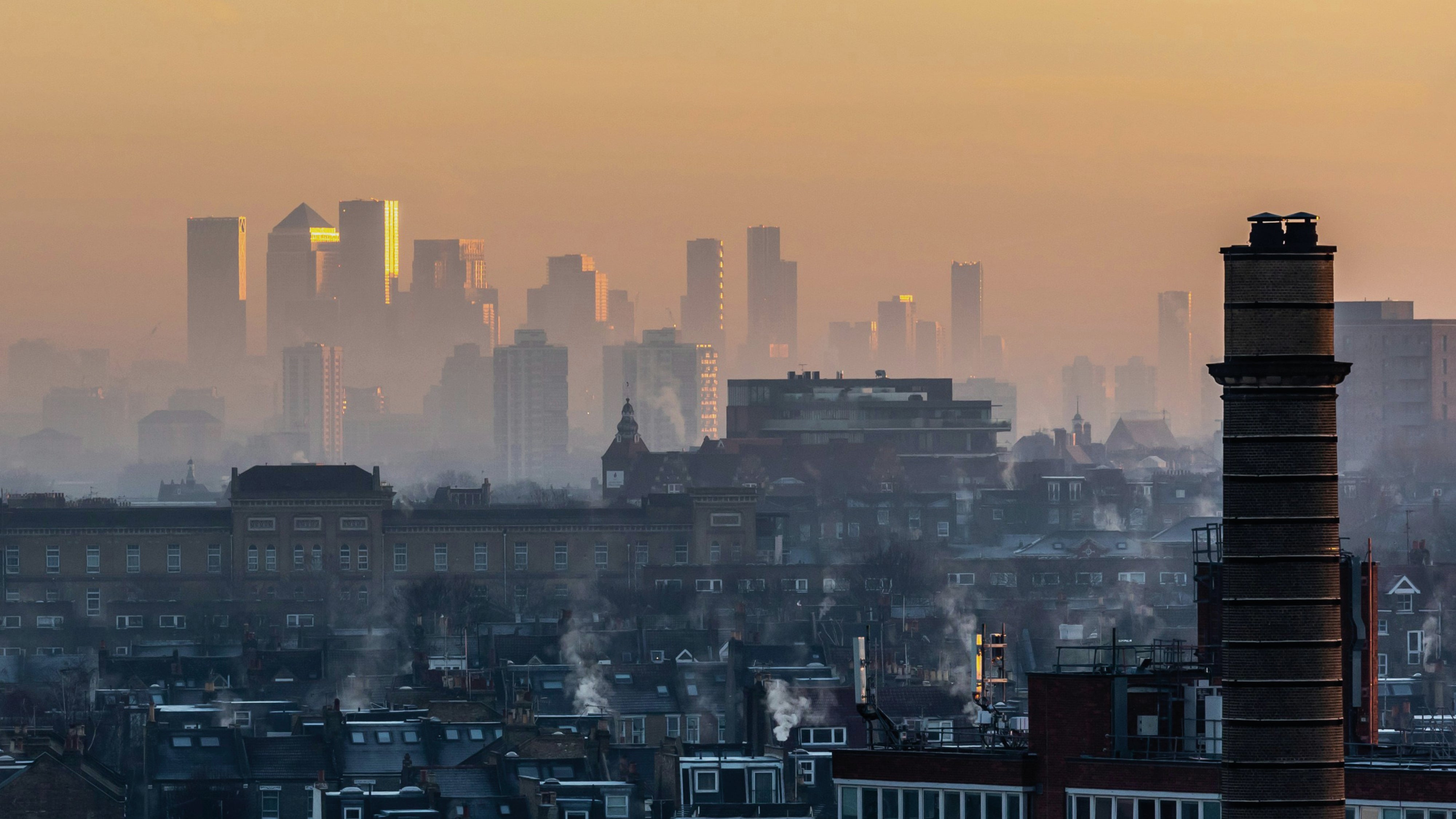
How air pollution affects the body
The most significant sources of air pollution in the UK are from road transport, cars, lorries, and buses releasing harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides and tiny particles that pollute the air. Other sources can be cigarette smoke, vaping as well as synthetic fragrances such as from candles. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is one of the most harmful components of air pollution.
When inhaled, these microscopic particles can:
- Trigger oxidative stress and inflammation
- Disrupt DNA expression through epigenetic changes (DNA methylation)
- Affect the cardiovascular system, reducing heart rate variability
-
Increase long-term risk of cognitive decline and dementia
The role of B vitamins
Folate, B6, and B12, show promise in reducing the impact of pollution on the body at a cellular level. B vitamins are essential for methylation, a key process that regulates gene activity and protects DNA.
Research shows they may buffer some of the negative effects of pollution:
DNA protection
In one human trial, supplementation with folate, B6, and B12 reversed pollution-induced DNA methylation changes, essentially “resetting” normal gene expression.
Cardiovascular resilience
The same study found that B vitamins preserved heart rate variability in participants exposed to fine particles, supporting cardiovascular stability.
Brain health
Long-term studies suggest that higher intake of folate and B12 may reduce the dementia risk associated with air pollution, likely by reducing homocysteine and protecting vascular integrity.
Food sources of B vitamins
Folate
Dark leafy greens, legumes, asparagus, avocado
Vitamin B6
Poultry, fish, bananas, potatoes, sunflower seeds
Vitamin B12
Meat, fish, dairy, and eggs
Supplementation considerations
- A balanced B complex ensures synergy between the different B vitamins.
- Dosages used in research trials are often higher than standard multivitamins, so therapeutic levels may need to be more than just the RDA.
-
Since B12 absorption can decline with age, older adults may especially benefit from supplementation.
Shop Advanced-B
The bigger picture
References
- Zhong J et al. B vitamins attenuate the epigenetic effects of ambient fine particles in a pilot human intervention trial. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017.
- Calderón-Garcidueñas L et al. Air pollution, cognitive deficits and the protective role of B vitamins. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019.
- Stover PJ. Folate and B12 metabolism in the context of pollution exposure. Nutr Rev. 2020.
- Chen R et al. Ambient air pollution and heart rate variability in humans: effect modification by folate and vitamin B12. Environ Health Perspect. 2012.